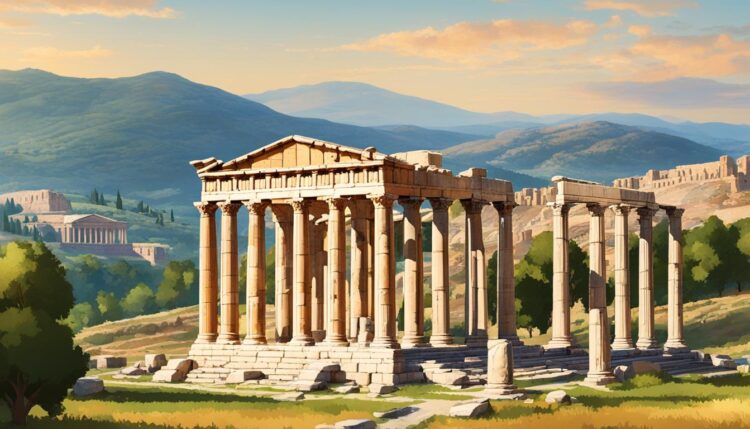
Have you ever wondered what hidden secrets lie in the remnants of the Temple of Artemis at Ephesus, one of the ancient wonders of the world?
Nestled near the modern town of Selçuk in Turkey, the historical city of Ephesus was once graced by the splendid Temple of Artemis. As one of the most impressive examples of Greek architecture, this grand sanctuary was dedicated to the goddess Artemis—a figure of immense reverence akin to the Roman goddess Diana. Despite its glory, by AD 401, the temple was reduced to ruins, with only its foundations and a few scattered fragments remaining.
Join us as we delve into the intricate past and captivating mysteries of this iconic monument, exploring why it stood as a beacon of divine worship and architectural marvel across the ancient world.
The Significance of the Temple of Artemis
Renowned for its majestic scale and religious importance, the Temple of Artemis at Ephesus holds a venerable place among the Seven Wonders of the Ancient World. This remarkable religious monument is a profound testament to the art, culture, and devotion of the ancient Greek civilization, immortalizing its significance in the annals of history.
Constructed with grandeur, the sanctuary not only showcased architectural excellence but also symbolized the cultural heritage of various civilizations that contributed to its creation and restoration over centuries. Its inclusion in the list of the Seven Wonders by Antipater of Sidon stands as a testament to its unmatched splendor.
Historical Background
The Temple of Artemis was initially funded by Croesus of Lydia and later reconstructed multiple times due to destruction caused by natural and man-made events. This monument was not just an architectural marvel but also a pivotal center for worship, reflecting the religious fervor of the ancient Greek civilization. Its presence in Ephesus attracted pilgrims and visitors, further enhancing its cultural heritage and global renown.
The Architecture of the Temple of Artemis
The Temple of Artemis, one of the Seven Wonders of the Ancient World, stands as a testament to the ingenuity of its architects, Chersiphron and his son Metagenes. This architectural marvel was remarkable not just for its grandeur but also for its meticulous design and proportionate dimensions.
Design and Dimensions
The Temple boasted an impressive marble construction, with dimensions of 377 feet in length and 151 feet in width, establishing an overwhelming presence in the ancient sanctuary. The layout featured two rows of towering Ionic columns, each standing 40 feet tall, which framed a ceremonial passage around the central cella that housed the cult image of Artemis. These Ionic columns, known for their scroll-like volutes, added to the temple’s aesthetic and structural grace, firmly entrenching its status as an ancient architectural marvel.
The blend of large-scale design and intricate details seen in the temple exemplified the sophistication of Greek architects. They employed advanced techniques and precise measurements to ensure that the temple reflected divine harmony and balanced beauty, qualities highly valued in Greek culture. This dedication to both form and function is what makes the edifice an enduring architectural marvel even in modern times.
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Length | 377 feet |
| Width | 151 feet |
| Number of Ionic Columns | Two rows |
| Height of Columns | 40 feet |
Location and Historical Context
The Temple of Artemis was strategically positioned in the ancient city of Ephesus, which is situated near modern-day Izmir, Turkey. This renowned archaeological site embodies a significant historical and cultural context that goes far beyond its Greek inception, extending to the Bronze Age. The ancient Efes location highlights the city’s expansive historical depth, attracting numerous cultural tourism enthusiasts. Despite being prone to flooding and presenting ongoing challenges to maintain its foundational integrity, the religious fidelity to this site ensured its ongoing sacred importance throughout centuries.
Ephesus stood as a pertinent example of an intersection between civilizations, cultures, and epochs, making it a vital destination for cultural tourism in Turkey. It serves as a window into the complexities and continuities of human civilization, particularly in how ancient societies intertwined their spiritual beliefs with their architectural grandeur.
Construction and Rebuilding Efforts through the Ages
The awe-inspiring Temple of Artemis at Ephesus underwent multiple phases of construction and rebuilding, highlighting its historical and religious importance. Each phase of this ancient construction marked a significant era in history, characterized by resilience and renewal.
Among its most notable contributors was Croesus of Lydia, who generously funded the construction of a magnificent marble temple. This particular historic restoration reinforced Ephesus’s standing as a cultural and spiritual beacon of the ancient world. However, tragedy struck in 356 BC when the temple was consumed in an act of arson, forever etching its story into the annals of archaeological significance.
The temple did not remain in ruins for long. With the ascendancy of Alexander the Great, efforts for reconstructing the temple were initiated, envisioning an even more grandiose structure. This period witnessed unparalleled architectural developments and extensive rebuilding that integrated a stunning array of columns, making the Temple of Artemis a marvel of ancient construction. It soon became a pivotal attraction for merchants, explorers, and devotees from across the ancient world.
Below is a comparative assessment highlighting the key phases and contributions in the construction and rebuilding of the Temple of Artemis:
| Phase | Contributor | Significant Elements |
|---|---|---|
| Initial Construction | Croesus of Lydia | Marble Temple |
| Post-Arson Reconstruction | Post-Alexander Era | Extensive column array |
This cycle of destruction and rebuilding underscores the temple’s profound archaeological significance. Each restoration effort not only preserved its majestic heritage but also elevated its stature in the pantheon of ancient wonders.
The Role of Croesus and Early Temples
The rise of the Temple of Artemis was closely tied to Croesus, the Lydian monarch renowned for his wealth, who significantly contributed to its construction during the 6th century BC. The site’s importance is exemplified by previous temple constructions that date back to the pre-Ionic era, mythically attributed to the Amazons.
Early Structures
Prior iterations of the temple, though less enduring, laid the initial temple foundations, underscoring the ongoing significance of ancient worship at the site. These early structures were pivotal in setting the stage for later construction successes. Archaeological findings reveal that the switch to marble marked a significant stylistic and engineering advancement, indicative of growing sophistication.
The Lydian influence, specifically during the era of King Croesus, heralded a new era of architectural grandeur. The implementation of marble and sturdier materials transformed the temple, reflecting both the technological advancements and religious devotion of the period.
Religious Significance and Worship at the Temple
The Temple of Artemis at Ephesus served as a vital epicenter for pilgrimages and goddess worship in the ancient world. Enshrined within its sacred grounds was an awe-inspiring statue of Artemis, believed to be a celestial embodiment of the divine.
Engaging in ancient rituals at the temple, worshippers sought the blessings of Artemis, especially in areas concerning nature and childbirth. The structure’s majestic presence attracted countless devotees, making it a focal point for cultural rites and spiritual ceremonies.

Within the temple’s hallowed walls, the interaction between mortals and the divine unfolded through elaborate rites and offerings. This profound connection left an indelible mark on the religious traditions of the time, enriching the cultural heritage associated with Artemis worship and ensuring its prominence in the annals of history.
The significance of the temple extended beyond its physical grandeur, symbolizing the protective aura of Artemis over her devotees. Those participating in pilgrimages contributed to a vibrant tapestry of religious practices, offering a glimpse into the devout lives of ancient societies drawn to this magnificent sanctuary.
| Aspect | Religious Practice |
|---|---|
| Pilgrimages | Annual journeys to seek divine favor |
| Goddess Worship | Prayers and offerings to Artemis |
| Ancient Rituals | Sacred ceremonies performed by priests |
| Cultural Rites | Community celebrations and spiritual observances |
Notable Art and Sculpture of the Temple
The Temple of Artemis at Ephesus was renowned for its extensive collection of ancient artwork and sculptural masterpieces, making it a marvel of both religious significance and artistic innovation. Within its sacred precincts resided numerous cultural artifacts that illustrated the grandeur of this iconic sanctuary.
Famous Statues
A central highlight was the distinctive statue of Artemis herself, which stood as a testament to the intricate goddess iconography. The figure was symbolically adorned with multiple breasts, representing fertility and abundance, and was festooned with animal reliefs, showcasing her dominion over wildlife and nature.
Relief Carvings
The temple’s architectural elements, including its stately columns, were replete with finely wrought relief carvings. These carvings depicted various mythological narratives, celebrating the goddess’s exploits and cementing her pivotal role in ancient culture. Each relief served not only as an embellishment but also as a vital storytelling medium, capturing the essence of the divine and the legendary.
| Artwork | Description | Symbolism |
|---|---|---|
| Statue of Artemis | An intricate statue with multiple breasts and animal reliefs | Fertility, abundance, nature |
| Column Reliefs | Finely wrought carvings on columns | Mythological narratives, divine glory |
The blend of cultural artifacts and sculptural masterpieces within the Temple of Artemis not only embellished the sacred space but also immortalized the ancient stories and iconography associated with the goddess. Each piece of ancient artwork played a role in making the temple a beacon of artistic and religious splendor.
Destruction and Final Decline
The Temple of Artemis faced immense historical devastation over the centuries. The most notorious event was caused by Herostratus, who set the temple aflame in 356 BCE to etch his name into history. This tragic act of arson was motivated by a desire for immortal fame, marking the first major blow to the once majestic structure.
Despite efforts to rebuild, the temple endured further ancient calamities, including invasions that left its grandiose pillars in ruins. One of the most brutal attacks came from the Goths in 267 CE, which significantly contributed to its ultimate downfall.
Following these repeated ancient calamities, the rise of Christianity in Ephesus played a pivotal role in the temple’s final abandonment. As the city embraced its new religious identity, the pagan site was neglected, and over time, the remnants of this grand edifice became scattered temple ruins, whispering of its glorious past.
| Events | Impact on the Temple |
|---|---|
| Arson by Herostratus (356 BCE) | First major destruction |
| Gothic Invasion (267 CE) | Severe damage and looting |
| Rise of Christianity | Site abandonment and decline |
The Rediscovery and Excavation of the Temple Site
Unearthing the grandeur of the Temple of Artemis at Ephesus was a long-awaited historic discovery. In 1869, John Turtle Wood, an architect and archaeologist under the patronage of the British Museum, embarked on an ambitious archaeological exploration that changed history. His expedition marked the rebirth of this ancient wonder from oblivion.
Key Excavations
The exploration, not without its trials, resulted in uncovering the temple’s foundations, which had been buried for centuries. Wood’s persistence paid off, revealing substantial archaeological insights that captured imaginations worldwide. The historic discovery of the temple’s remnants offered a glimpse into its construction and cultural significance, solidifying Ephesus’s status as a site of great historical import. The excavation projects orchestrated by Wood and subsequent archaeologists have been pivotal in illuminating a previously concealed chapter of human history.
These discoveries continue to attract scholarly attention and tourist admiration, making the Temple of Artemis a focal point for both academic study and cultural tourism. The systematic excavation projects unearthed not only the architectural marvels but also relics that provide context to the daily lives and religious practices of the ancient Ephesians. Such findings underscore the temple’s significance in the broader narrative of ancient history and archaeology.