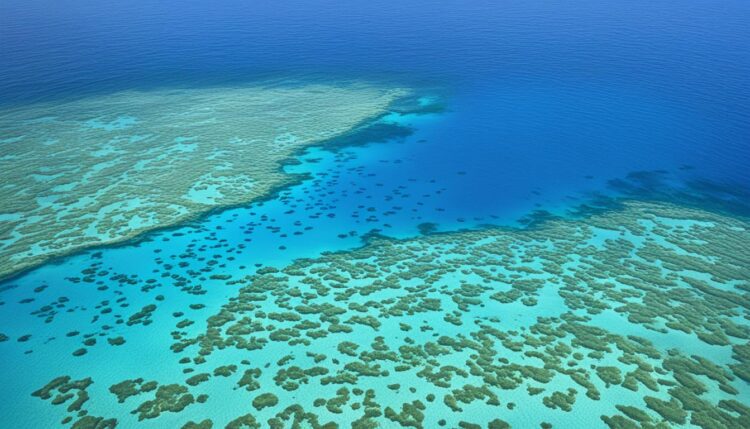
Marine Protected Areas (MPAs) play a crucial role in ocean conservation and environmental protection. These specially designated oceanic reserves regulate human activities to safeguard marine ecosystems from threats such as overfishing, pollution, and climate change. MPAs are diverse in the level of restrictions imposed, ranging from areas that allow sustainable use to zones where human entry is entirely prohibited.
Globally, over 5,000 MPAs have been established, covering more than 8% of the ocean. By implementing these protected areas, we can help reverse the decline in marine species populations, preserve habitats, and support the economies of coastal communities through sustainable fishing and tourism. The global effort to create and maintain MPAs underscores the serious commitment to environmental protection and the preservation of our world’s oceans.
Key Takeaways
- Marine Protected Areas (MPAs) are essential for ocean conservation and environmental protection.
- MPAs regulate human activities to prevent environmental damage.
- Over 5,000 MPAs have been established worldwide, covering more than 8% of the ocean.
- MPAs help address threats like overfishing, pollution, and climate change.
- These areas support sustainable fishing and tourism for coastal communities.
What are Marine Protected Areas (MPAs)?
Marine Protected Areas (MPAs) are specially designated regions in oceans, seas, and large lakes where human activities are regulated to preserve natural resources and biodiversity. These areas are critical for maintaining healthy marine ecosystems and ensuring the sustainability of marine life.
Definitions and Types
MPAs vary in their levels of protection and permissible activities. Common types include marine parks, marine reserves, and marine sanctuaries. Marine parks allow limited human activities, whereas marine reserves and marine sanctuaries typically impose stricter regulations to ensure environmental preservation. Another crucial type is the no-take zone, which completely prohibits extractive activities like fishing and mining.
Goals of MPAs
The primary goals of MPAs include the conservation of marine biodiversity, protection of endangered species, and restoration of overfished populations. These areas also support scientific research, sustainable tourism, and the protection of cultural heritage sites. By preserving critical habitats, MPAs play a vital role in maintaining ecological balance.
Global Presence
With over 5,000 MPAs worldwide, these protected regions are crucial for the global effort to safeguard the marine environment. Notable examples include the Great Barrier Reef Marine Park in Australia and the Papahānaumokuākea Marine National Monument in Hawaii. The distribution and effectiveness of MPAs vary globally, reflecting different levels of commitment and resources allocated by individual countries.
| Type of MPA | Protection Level | Permissible Activities |
|---|---|---|
| Marine Park | Moderate | Recreational activities, limited fishing |
| Marine Reserve | High | Scientific research, no commercial activities |
| Marine Sanctuary | High | Recreational activities, restricted fishing |
| No-Take Zone | Very High | No extractive activities |
The Role of Coral Reefs in MPAs
Marine Protected Areas (MPAs) play a significant role in the preservation and protection of coral reef ecosystems. By safeguarding these vibrant marine habitats, MPAs contribute to both coral preservation and broader marine habitat conservation efforts. Coral reefs serve as vital ecosystems that support a vast array of marine life, making their protection essential for maintaining biodiversity and ecological balance.
Coral Reef Ecosystems
Coral reef ecosystems are among the most diverse and valuable marine habitats on the planet. These ecosystems provide shelter, food, and breeding grounds for thousands of marine species, including fish, invertebrates, and algae. Notably, reefs situated within MPAs, such as those near the Galápagos Islands, exemplify the profound biodiversity they harbor. The structured environments created by corals enhance marine habitat conservation, supporting species that may not thrive in other settings.
Benefits of Protecting Coral Reefs
Protecting coral reefs within MPAs offers numerous benefits. Coral preservation is critical for maintaining healthy fish populations, as many fish species depend on coral reefs during their life cycles. Additionally, well-preserved coral reefs can bolster local economies through tourism and recreational activities, creating sustainable sources of income for communities. Consequently, MPAs that focus on coral reef protection contribute to ecological, economic, and social sustainability.
| Benefits of Coral Reef Protection | Description |
|---|---|
| Biodiversity Support | Coral reefs provide habitats for a wide range of marine species, promoting biodiversity. |
| Economic Gain | Healthy reefs attract tourism and recreational activities, supporting local economies. |
| Ecological Balance | Reefs contribute to marine habitat conservation, maintaining ecological balance. |
How Marine Protected Areas Help Combat Marine Pollution
Marine Protected Areas (MPAs) play an essential role in preserving ocean health by addressing various pollution sources and implementing effective control measures. These regulated zones are crucial for achieving significant pollution reduction and ensuring sustainable marine environmental management.
Sources of Marine Pollution
Marine pollution originates from numerous sources, such as industrial discharge, agricultural runoff, and maritime activities. Plastics, chemical contaminants, and oil spills are some of the main pollutants that severely affect marine ecosystems. These pollutants not only harm aquatic life but also disrupt the balance of marine habitats.
Pollution Control Measures in MPAs
MPAs adopt stringent regulations to mitigate pollution effectively. These measures include:
- Waste Management: Implementation of waste management programs to control and reduce waste entering marine environments.
- Water Quality Monitoring: Regular monitoring and assessment of water quality to detect and address pollution sources promptly.
- Regulation of Human Activities: Restrictions on fishing, boating, and industrial operations to minimize the release of pollutants.
- Conservation Programs: Initiatives aimed at restoring endangered species and habitats affected by pollution.
Through these strategies, MPAs contribute significantly to pollution reduction, fostering a healthier and more resilient marine ecosystem. By prioritizing marine environmental management, MPAs ensure the long-term protection of our oceans from the detrimental effects of pollution.
Protecting Marine Biodiversity
Marine Protected Areas (MPAs) play a crucial role in preserving oceanic biodiversity. By implementing strict conservation measures, they foster a thriving environment for various marine species and bolster habitat protection.
Species Conservation
The primary goal of MPAs is to protect endangered marine species. These designated zones provide a sanctuary where human activities like overfishing and commercial exploitation are heavily regulated or prohibited. The Galápagos Marine Reserve, for instance, is home to unique species such as the Galápagos penguin and hammerhead sharks, both of which thrive under the protected status.
Habitats Supported by MPAs
MPAs also contribute significantly to habitat protection. Coral reefs, seagrass beds, and mangroves are essential habitats supported within these areas. These environments not only harbor a rich variety of marine life but also act as nurseries for many fish species. The USS Monitor National Marine Sanctuary, safeguarding the historic shipwreck and its surrounding ecosystem, provides a pristine habitat for numerous sea creatures, thus showcasing the importance of habitat conservation within these protected marine zones.
| MPA | Key Species | Habitat Type |
|---|---|---|
| Galápagos Marine Reserve | Penguins, Hammerhead Sharks | Coral Reefs |
| USS Monitor National Marine Sanctuary | Various Fish Species | Shipwreck Ecosystem |
The Economic Benefits of MPAs
The establishment of Marine Protected Areas (MPAs) extends beyond environmental conservation, ushering significant economic advantages. Notably, these benefits bolster both eco-tourism and fishing industry sustainability through enhanced regulatory frameworks and conservation efforts.
Tourism and Recreation
MPAs draw tourists and recreation enthusiasts due to their pristine conditions and thriving marine life. Eco-tourism has flourished in these regions, offering activities like scuba diving, snorkeling, and marine wildlife viewing. The influx of tourists translates into revenue for local businesses, from hospitality to guided tours, supporting the economies of coastal communities.
“Marine Protected Areas are essential for preserving the natural beauty of our oceans. They attract tourists and provide sustainable income for local communities, advancing both environmental and economic objectives.”
Sustainable Fisheries
The introduction of MPAs has contributed significantly to the sustainability of the fishing industry. Within protected bounds, fish populations flourish due to reduced fishing pressure, leading to a spillover effect where fish migrate into adjacent fishing areas. This enhances fishing yields, ensuring the long-term viability of fisheries. By promoting fishing industry sustainability, MPAs help maintain the livelihood of fishermen while preserving marine ecosystems.
- Enhanced fish populations within MPAs.
- Improved fishing yields in surrounding areas.
- Long-term sustainability of the fishing industry.
By creating a balance between conservation and economic activity, MPAs present a compelling case for their expansion and support worldwide.
Community Involvement in MPA Management
Engagement at the local level is crucial for the successful management of Marine Protected Areas (MPAs). By integrating local knowledge and fostering community involvement, MPAs can achieve and sustain their conservation objectives.
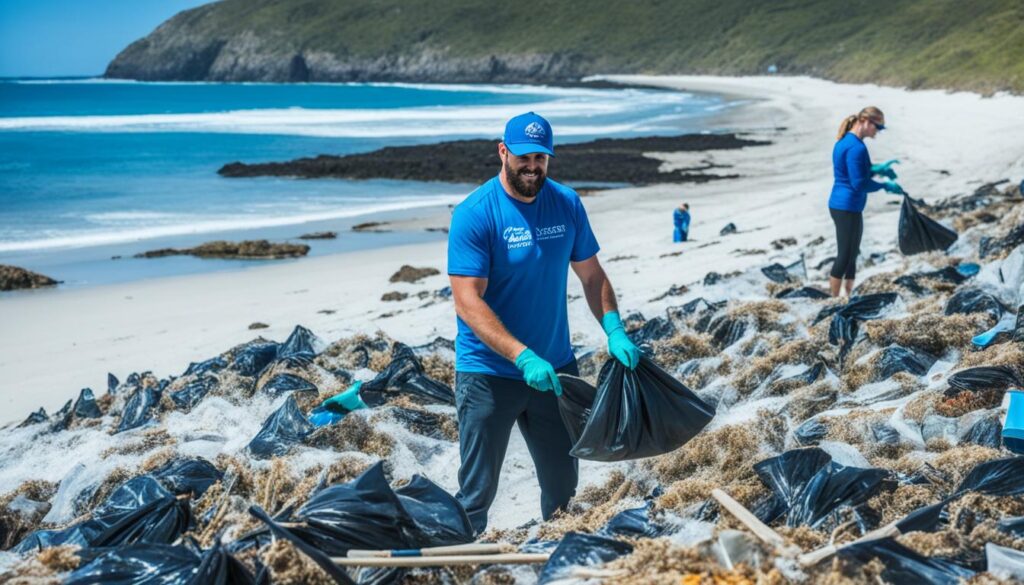

Local Community Participation
Local communities are often the first line of defense in preserving marine resources. Participation in patrols, restoration projects, and resource monitoring are some ways communities contribute to local conservation efforts. In Honduras, community-supported patrolling programs have proven to be effective in reducing illegal fishing activities and promoting sustainable practices.
Indigenous Knowledge and Conservation
Indigenous stewardship plays a significant role in the management of MPAs. Indigenous peoples bring centuries-old wisdom and practices that are essential for the ecological well-being of marine environments. Their traditional methods, combined with modern conservation techniques, enhance biodiversity and ensure the sustainability of these areas. Acknowledging and integrating indigenous stewardship in MPA processes not only respects cultural heritage but also supports more effective conservation outcomes.
Successful Examples of Marine Protected Areas
Marine Protected Areas (MPAs) are vital in conserving marine ecosystems and biodiversity. Two standout examples showcasing effective marine conservation are the Galápagos Marine Reserve and the Great Barrier Reef Marine Park.
Galápagos Marine Reserve
The Galápagos Marine Reserve, a UNESCO World Heritage site, represents a pinnacle of Galápagos conservation success. The reserve spans over 133,000 square kilometers and encompasses diverse marine habitats. Effective zoning and strict regulations have led to remarkable recovery in marine species.
By implementing stringent controls on fishing and other human activities, the Galápagos Marine Reserve has enabled a significant increase in the populations of species such as the green sea turtle and the Galápagos shark. Conservation efforts have not only improved biodiversity but also boosted eco-tourism, enhancing local economies.
Great Barrier Reef Marine Park
The Great Barrier Reef Marine Park is another exemplary illustration of marine protection. Covering over 344,000 square kilometers, it is the largest coral reef system in the world. The park’s management focuses on Great Barrier Reef protection through zoning regulations and initiatives aimed at reducing human impact.
Conservation measures have significantly benefited both the reef’s health and the surrounding marine life. The efforts in Great Barrier Reef protection have seen a rise in coral cover and increased populations of marine species. Moreover, the park’s success story underscores the importance of governmental and communal collaboration in marine conservation.
| Marine Protected Area | Size (sq km) | Main Conservation Achievements |
|---|---|---|
| Galápagos Marine Reserve | 133,000 | Increased populations of marine species, enhanced eco-tourism |
| Great Barrier Reef Marine Park | 344,000 | Increased coral cover, marine species population growth |
Challenges and Threats to MPAs
Marine Protected Areas (MPAs) are critical in preserving ocean ecosystems, but they face numerous challenges and threats. Implementing and maintaining these areas is a complex task that requires addressing issues such as overfishing and climate change. These pervasive threats can undermine the effectiveness of MPAs, impacting their ability to safeguard marine biodiversity and support climate resilience.
Overfishing
Overfishing remains one of the most significant threats to the success of MPAs. The impact on fish populations can be dire, leading to diminished biodiversity and ecosystem health. Overexploitation of marine resources not only disrupts the food webs but also reduces the resilience of these ecosystems to environmental changes. Many MPAs combat overfishing through strict regulations that include designated no-take zones, seasonal closures, and quotas. Enforcing these regulations, while challenging, is essential for sustaining fish populations and preserving the ecological balance within MPAs.
Climate Change
Climate change poses another formidable threat to the integrity of MPAs. Rising sea temperatures, ocean acidification, and extreme weather events can severely degrade marine habitats. Coral reefs, in particular, are highly susceptible to bleaching events caused by increased water temperatures. MPAs must therefore implement adaptive management strategies to bolster climate resilience. This includes monitoring environmental changes, restoring damaged habitats, and enhancing the genetic diversity of protected species. By focusing on these measures, MPAs can better withstand the adverse effects of climate change and continue to provide a refuge for marine life.
Addressing the challenges of overfishing and climate change is crucial for the efficacy of Marine Protected Areas. Through diligent management and strategic interventions, MPAs can enhance their role in ecosystem preservation, supporting both biodiversity and climate resilience.
FAQ
What are Marine Protected Areas (MPAs)?
Why are Marine Protected Areas important for ocean conservation?
How do MPAs combat marine pollution?
What role do coral reefs play in Marine Protected Areas?
How do MPAs benefit coastal communities economically?
How do local communities participate in MPA management?
What are some successful examples of MPAs?
What challenges do MPAs face?
Source Links
- https://education.nationalgeographic.org/resource/importance-marine-protected-areas/
- https://coral.org/en/blog/the-importance-of-marine-protected-areas-mpas/
- https://www.pewtrusts.org/en/research-and-analysis/issue-briefs/2022/07/connecting-marine-protected-areas-can-improve-ocean-health
- https://www.consumernotice.org/environmental/pollution-reduction/
- https://www.consumernotice.org/environmental/water-contamination/pfas/